Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women. In 2018, an estimated
570 000 women were diagnosed with cervical cancer worldwide and about 311 000 women died from the disease.
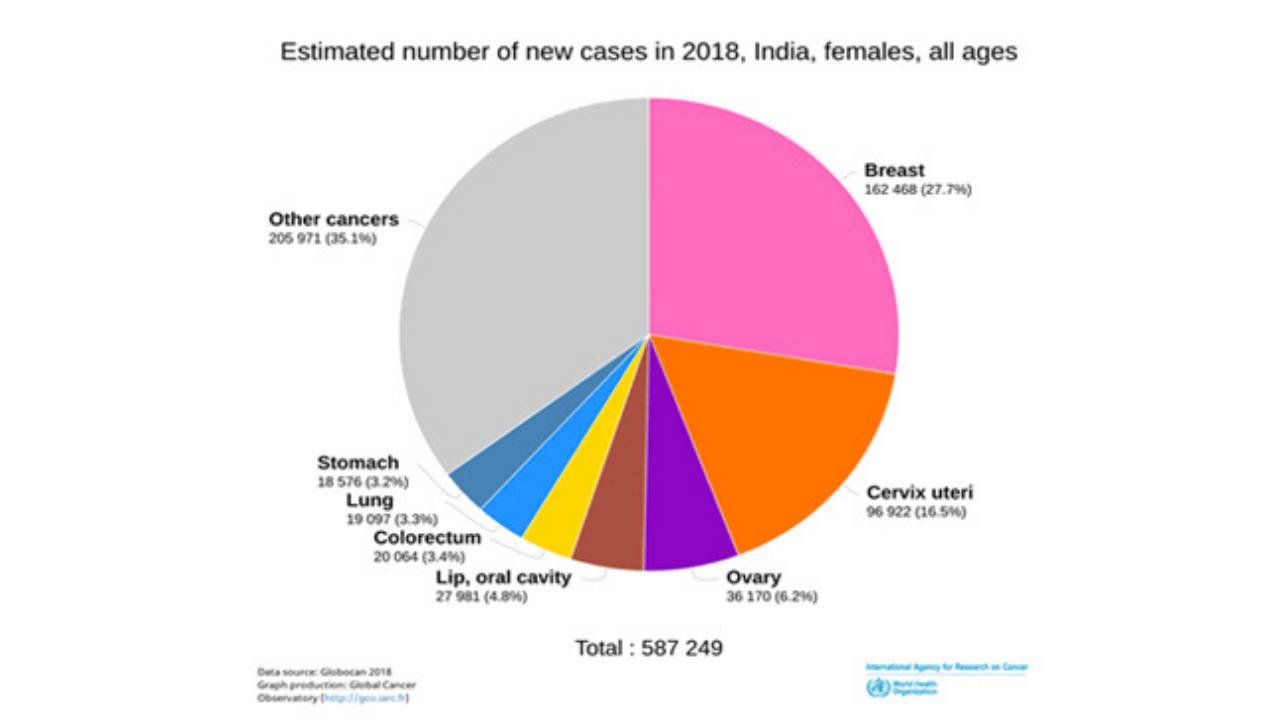
In India cervical cancer is the second most common malignancy among females.
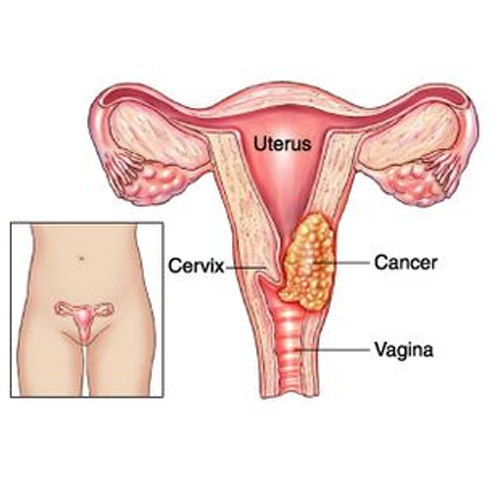
Almost all cervical cancer cases (99%) are linked to infection with high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV), an extremely common virus transmitted through sexual contact.
Although most infections with HPV resolve spontaneously and cause no symptoms, persistent infection can cause cervical cancer in women.
Effective primary (HPV vaccination) and secondary prevention approaches (screening for, and treating precancerous lesions) will prevent most cervical cancer cases.
When diagnosed, cervical cancer is one of the most successfully treatable forms of cancer,as long as it is detected early and managed effectively. Cancers diagnosed in late stages can also be controlled with appropriate treatment and palliative care.
With a comprehensive approach to prevent, screen and treat, cervical cancer can be eliminated as a public health problem within a generation.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) initially recommended the vaccine for all people aged 9–26 years. However, the CDC now advise that the vaccine is also available for all women and men aged 26-45, who did receive the vaccine as a preteen.
Women should have regular cervical smear tests, or Pap test. A Pap test is preventive. It aims not to detect cancer but to reveal any cell changes that indicate the possible development of cancer so that action can be taken early.


In the early stages of cervical cancer, a person may experience no symptoms at all.
The common symptoms of cervical cancer are:
Anyone who experiences any of these symptoms should see a doctor.
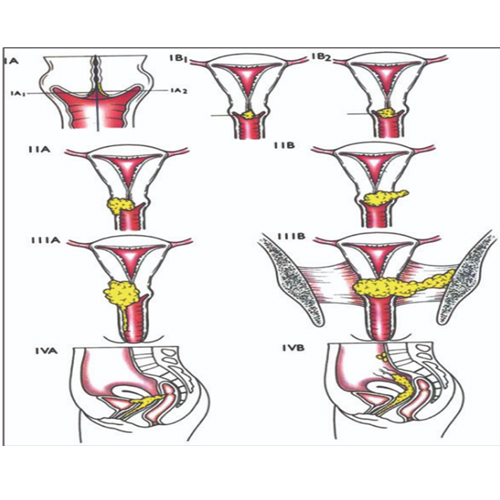
Staging aims to assess how far the cancer has spread and whether it has reached nearby structures or more distant organs. It helps to decide the most effective type of treatment.
Undergoing screening and seeking medical attention if any symptoms occur can help a person access early treatment and increase the chances of survival.
Cervical cancer treatment options include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy or combinations of these.
Deciding on the kind of treatment depends on several factors, such as the stage of the cancer, as well as age and overall state of health.
Surgery is a common treatment method for very early stages when the cancer has not spread beyond the cervix.
For locally advanced cases when the cancer has spread beyond the cervix, surgery is not usually an option and typically involve either radiation therapy or a combination of radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
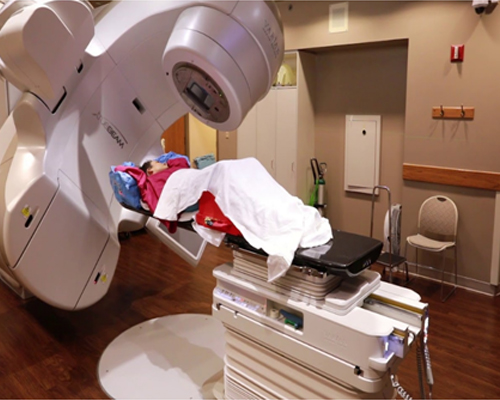
In the later stages of cancer, professionals provide palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
if you have any Emerangcy by health problem contact this No. (+91) 7980 408 683 / 9830 158 619 or contact form
© 2021, All rights reserved by Dr. Sanjoy Roy